Mixformer
MixFormer: End-to-End Tracking with Iterative Mixed Attention[1]
作者是来自南大的Yutao Cui, Cheng Jiang, Limin Wang, Gangshan Wu. 论文引用[1]:Cui, Yutao et al. “MixFormer: End-to-End Tracking with Iterative Mixed Attention.” 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2022): 13598-13608.
Time
- 2022.Mar
Key Words
- compact tracking framework
- unify the feature extraction and target integration solely with a transformer-based architecture
VOT,MOT,SOT的区别
- VOT是标首帧,MOT是多目标追踪,SOT是单目标追踪。
动机
Tracking经常用多阶段的pipeline:feature extraction,target information integration,bounding box estimation。为了简化这个pipeline,作者提出了一个紧凑的tracking框架,名为MixFormer。
target information integration解释: fuse the target and search region information
总结
核心设计利用是attentation操作的灵活,提出了Mixed Attention Module(MAM) for simultaneous feature extraction and target information integration. 这个即时的modeling scheme,能够抽取target-specific discriminative features以及在target和search area之间能够进行大量的communication。基于MAM,通过堆叠MAMs with progressive patch embedding 和place a localization head on top,来构建MixFormer追踪框架。
为了在online tracking的时候处理多个目标的template,在MAM中设计了一个非对称的注意力,来减小计算成本,提出了一个有效的score prediction module来选择高质量的template。
视觉目标追踪的仍然是有很多挑战,包括:scale variations, object deformations, occlusions, confusion from similar objects.
之前的流行的trackers通常包括几个部分:
- a backbone 来提取tracking target和 search area 的feature,
- 为了后续的target-aware的定位,一个集成的模块(integration module)来使得tracking target和search area进行信息交流
- task-specific heads来精确地定位目标和估计bounding box.
集成模块(integration moduel) 是追踪算法的关键,它能够整合target information,在通用特征提取和目标感知定位架起桥梁。传统的集成方法包括correlation-based operations(e.g., SiamFC, SiamRPN, CRPN, SiamFC++, 将Simaese 网络和correlation操作结合起来,对target和search之间的全局依赖进行建模), online learning 算法(e.g., DCF, KCF, ATOM, FCOT, 对于有区别的tracking,学习到独立于目标的model),最近,多亏了全局和动态的modeling capacity,引入了transformer来进行基于注意力的integration,有了很好的效果(STMTrack, STARK),然而,这些基于transformer的trackers仍然基于CNN作为特征提取例如ResNet,仅仅用attention 操作 in the latter high-level and abstract representation space. CNN是有限的,它们通常用来pre-trained for 通用目标提取,可能忽略fine structure information for tracking. CNN用局部卷积核,缺乏全局建模能力。
为了解决以上问题,在tracking framework design上,提出了新的思路。通用特征提取和target information integration集成到一个统一的框架,coupled processing paradigm 有很多好的advantages:
- 能够使得feature extraction to be more specific to the corresponding tracking target and capture more target-specific discriminative features.
- 能够使得target information to be more extentively 集成到search area, 然后更好地capture their correlation
- 得到一个更为紧凑的tracking pipelien with a single backbone and tracking head, without an explicit integration module.
Attention module是一个非常灵活的架构,building block wiht dynamic and global modeling capacity, 提出了一个mixed attention module(MAM),能够同时进行特征提取和 mutual interaction of target template and search area。在MAM中,设计了一个混合的interaction scheme,包括自注意力和cross-attention operations on tokens from template and search area。自注意力能够抽取target or search area的自己的特征,然而cross-attention allows for communications between them(search and target area) to mix the target and search area informations。为了降低MAM的计算成本,能够使得多个templates 来处理obect deformation,提出了一个定制的非对称的attention scheme通过修建不必要的target-to-search area cross-attention.
MixFormer backone: 通过堆叠Patch embedding和MAM,最后放一个简单的localization head 来得到整个的tracking framework。 为了处理追踪过程中的目标变形,提出了基于target template update机制的score,MixFormer能够容易地适应multiple target template inputs.
最近的trackers引入了基于transformer的integration module,来得到更复杂的依赖(dependencies),实现更好的效果。
MAM的输入使target template和search area。旨在提取long-range特征,融合它们之间的特征。和原始的MHA不同,MAM执行dual attention operations on two separate tokens sequences of target template and search area. 对每个sequences上的tokens进行自注意力来得到target or search specific information;同时,对来自2个sequencnes的tokens进行cross attention来得到target template and search area的交互信息。通过拼接concatenated token sequences来进行mix attention mechanism.
给定一个concatenated tokens of multiple targets and search,首先将其分成2个部分,然后reshape成一个2D的feature map,为了实现additional modeling of local spatial context, 在每个feature map上用一个可分离的depth-wise convolutional projection layer. target 和search的每个feature map 然后通过linear project 来得到queries, keys, values of the attention operation. \(q_t, k_t, v_t\)代表target, \(q_s, k_s, v_s\)代表search region. mixed attention的定义如下: \[\begin{aligned}&k_{m}=\mathrm{Concat}(k_{t},k_{s}),\quad v_{m}=\mathrm{Concat}(v_{t},v_{s}),\\&\mathrm{Attention}_{\mathrm{t}}=\mathrm{Softmax}(\frac{q_{t}k_{m}^{T}}{\sqrt{d}})v_{m},\\&\mathrm{Attention}_{s}=\mathrm{Softmax}(\frac{q_{s}k_{m}^{T}}{\sqrt{d}})v_{m},\end{aligned}\]
- \(Attention_s\)和\(Attention_t\)包含了feature extraction和信息融合,最后,targets token 和search token通过一个linear projection 进行concatenated 和processed。
非对称的mixed attention scheme:通过剪掉不必要的target-to-search area cross-attention,降低了MAM的计算成本,能够高效地用multiple templates来处理目标变形的问题。
\[\begin{aligned}&k_{m}=\mathrm{Concat}(k_{t},k_{s}),\quad v_{m}=\mathrm{Concat}(v_{t},v_{s}),\\&\mathrm{Attention}_{\mathrm{t}}=\mathrm{Softmax}(\frac{q_{t}k_{m}^{T}}{\sqrt{d}})v_{m},\\&\mathrm{Attention}_{s}=\mathrm{Softmax}(\frac{q_{s}k_{m}^{T}}{\sqrt{d}})v_{m},\end{aligned}\]
Corner-based localization head: 受STARK的启发,用了全卷积的corner based localization head来估计tracked object的bounding box。通过计算corner probability distribution,来得到bounding box。
Query based localization head: 在最后一个stage的序列中,加了一个可学习的regression token,用这个token作为anchor来aggregate整个目标和搜索区域的信息。最后一个3个fc layers的FFN来回归bounding box。不需要后处理。
Training: 用CVT模型对MAM进行预训练,然后再整个目标dataset上进行微调。
Template Online Update: 这个再得到时序信息和处理目标形变、外观变化上很重要,在追踪的时候,低质量的templates可能导致较差的追踪性能。引入了一个score prediction module(SPM)。SPM由2个attention blocks,three-layer perceptron组成。一个可学习的score token和search ROI tokens进行attention,然后score token与初始目标的所有positions进行attention, implicitly compare mined target with first target. 最后,通过一个MLP和sigmoid来得到score,低于0.5的online template被视为negative.
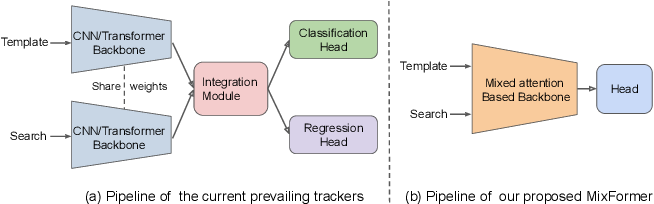 \(Fig.1^{[1]}\)
Comparison of tracking pipeline. (a) The dominant tracking framework
contains three components: a convolutional or transformer backbone, a
carefully-designed integration module, and task-specific heads. (b) Our
MixFormer is more compact and composed of two components: a
target-search mixed attention based backbone and a simple localization
head.
\(Fig.1^{[1]}\)
Comparison of tracking pipeline. (a) The dominant tracking framework
contains three components: a convolutional or transformer backbone, a
carefully-designed integration module, and task-specific heads. (b) Our
MixFormer is more compact and composed of two components: a
target-search mixed attention based backbone and a simple localization
head.
 \(Fig.2^{[2]}\) Mixed
Attention Module (MAM) is a flexible attention operation that unifies
the process of feature extraction and information integration for target
template and search area. This mixed attention has dual attention
operations where self-attention is performed to extract features from
itself while cross-attention is conducted to communicate between target
and search. This MAM could be easily implemented with a concatenated
token sequence. To further improve efficiency, we propose an asymmetric
MAM by pruning the target to-search cross attention (denoted by dashed
lines).
\(Fig.2^{[2]}\) Mixed
Attention Module (MAM) is a flexible attention operation that unifies
the process of feature extraction and information integration for target
template and search area. This mixed attention has dual attention
operations where self-attention is performed to extract features from
itself while cross-attention is conducted to communicate between target
and search. This MAM could be easily implemented with a concatenated
token sequence. To further improve efficiency, we propose an asymmetric
MAM by pruning the target to-search cross attention (denoted by dashed
lines).
 \(Fig.3^{[3]}\)
MixFormer presents a compact end-to-end framework for tracking without
explicitly decoupling steps of feature extraction and target information
integration. It is only composed of a single MAM backbone and a
localization head.
\(Fig.3^{[3]}\)
MixFormer presents a compact end-to-end framework for tracking without
explicitly decoupling steps of feature extraction and target information
integration. It is only composed of a single MAM backbone and a
localization head.
